Tax Time Reminder: Don’t Forget About Fringe Benefits
Share this article:
Rose Report: Issue 42

By Peter Stratos, Rose Financial Solutions Tax Partner
As 2020 nears its end, it’s time to focus on W-2 reporting and the tax implications of the fringe benefits you are providing your employees. According to the Internal Revenue Service’s (IRS) Publication 15-B, “a fringe benefit is a form of pay for the performance of services. For example, you provide an employee with a fringe benefit when you allow the employee to use a business vehicle to commute to and from work.”
Certain fringe benefits should be added to the taxable wages of all employees, including shareholders. These adjustments are to be made for employees of all entities, including both C and S corporations. The actual value of fringe benefits provided must be determined by January 31 of the year following receipt of the benefit.
Examples of Fringe Benefits
Value of personal use of company car – subject to FICA/Medicare, FUTA, FITW & SITW. However, FITW and SITW need not be withheld on that value if the employee is so notified by January 31 or within 30 days of the vehicle being provided by the employer. We have provided an example of this notification in Exhibit 1.
Employer-paid group-term life insurance over $50,000 – subject to FICA/Medicare. For coverage provided after January 1, 2020, use the rates listed on Exhibit 2. Note that the rates provided are the cost of $1,000 of coverage for one month. Accordingly, the W-2 inclusion will be equal to the amount of coverage exceeding $50,000, divided by $1,000, multiplied by the appropriate rate on Exhibit 1 for each month of coverage. Multiply that number by 12, if the employee was covered for the entire year, to derive the total amount.
Employee business expense reimbursements/allowances under a nonaccountable plan – subject to FICA/Medicare, FUTA. See below for an explanation of what should be included.
Expense reimbursements/allowances
If an employee received an allowance/reimbursement from the company for company related expenses, i.e., travel, a car, etc., then the amount should be included in the employee’s wages. If the employee gave an accounting of the expenses incurred or used IRS per diem amounts, i.e., filled out an expense voucher, and refunded any excess allowances/reimbursements to the company, then there is no amount to be added to the W-2. If, however, the employee kept any amounts in excess of the expenses accounted for or did not provide an accounting of the expenses incurred, all of the reimbursed expenses should be added to taxable wages on the W-2.
Worksheets
Below we have included four worksheets in Exhibit 3 to aid in calculating the value of personal use of the company car. The first worksheet is to be filled out by the employee and is used to calculate the percentage of personal use based on the employee’s analysis of total miles driven during the year. The next two worksheets are used to calculate the actual amounts to be included in the employee’s income. Please note that there are limitations on using Methods II and III. The fourth worksheet is used to determine the annual lease value to be used with Method I of calculating income from personal use of a company vehicle.
Accounting for adjustments
The following are three different methods to account for the fringe benefits:
- Gross up the fringe benefit to cover payroll taxes and add the grossed-up amount to the W-2 (see the example below).
- Treat the fringe benefit amount as the gross pay and withhold the corresponding payroll taxes from the employee’s last paycheck.
- Have the employee reimburse the company for the amount of the fringe benefit.
Gross up method
To gross up the employee’s W-2, the employee’s gross wages should be increased by the taxable fringe benefit, plus the related payroll taxes. An easy formula is to divide the fringe benefit amount by 100%-payroll tax %.
Example: An employee has a $2,000 value on the personal use of the corporate auto. The federal withholding will be 28% and the state withholding will be 5.75%. The amount is subject to FICA/Medicare taxes.
$2,000/(100%-28%-5.75%-7.65%) or $3,413
Therefore, the employee’s taxable wages are increased by $3,413 and his withholdings are increased by $1,413.
S corporation adjustments
In addition to the adjustments previously discussed, an S corporation must include certain fringe benefit items on the Forms W-2 of its more than 2% shareholders and family members who are also employees. These fringe benefits are generally excluded from income of other employees.
The includable fringe benefits are items paid by the company for:
- Medical, hospital, dental, and accident insurance premiums paid under a corporate plan – subject to FITW and SITW only
- Disability insurance premiums – subject to FICA/Medicare, FITW and SITW
- Group-term life insurance premiums- all are taxed, not just amounts in excess of $50,000 (do not include premiums on policies where the corporation is both the owner and beneficiary) – subject to FICA/Medicare.
Please call us if you have any questions.
EXHIBIT 1
Employer Election Not To Withhold on Vehicle Fringe Benefit
To whom it may concern: This is to advise you that [company name] will not withhold income tax on the value of an employee’s personal use of a truck or car provided by us. The fair market value of the benefit will, however, be included on the Form W-2 furnished to the employee for the year the vehicle was used. Affected employees may wish to pay the additional tax due by amending their Form W-4 to adjust their withholding allowance, or by increasing their quarterly estimated tax payments.
Very truly yours, /s/ _________________________________
EXHIBIT 2
EMPLOYER-PAID GROUP-TERM LIFE INSURANCE OVER $50,000
(cost per $1,000 for protection for one month)
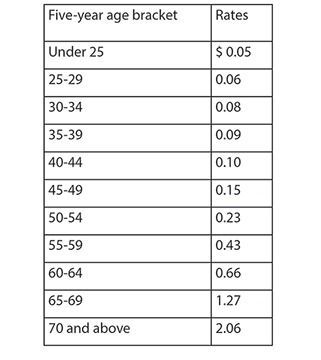
Exhibit 3
2020 Vehicle Policy and Income Inclusion Guide
Employer’s worksheet to calculate employee’s taxable income resulting from employer-provided vehicle for calendar year 2020 Employee
Description of vehicle
Date vehicle first made available to any employee
Date vehicle first made available to this employee
Select one method (note limitations on Methods II and III)
Method I — Annual lease value method for vehicles available 30 days or more. (For vehicles less than 30 days, see below)

Method II – Standard mileage rate method
Generally, in order to qualify to use the cents-per-mile method, the vehicle must: (1) be expected to be regularly used in the employer’s business throughout the calendar year or (2) be driven at least 10,000 miles per year and (3) on the date it is first made available to any employee for personal use, the standard automobile cost may not exceed the value of $50,400 for passenger automobiles (including trucks and vans) placed in service on or after Jan. 1, 2019. Once this method is adopted for a particular vehicle, it must be continued until the vehicle no longer qualifies.
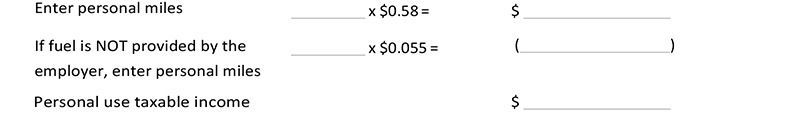
Method III – Special commuting method
This method may only be used for vehicles covered by a written policy that allows commuting but no other personal use.Do not use this method if the employee is a “control employee” (i.e., he or she is a 1% or more owner, a director, anofficer with compensation of $110,000 or more or an individual with compensation equaling or exceeding $225,000).
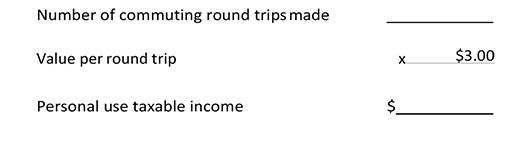
Annual lease value table
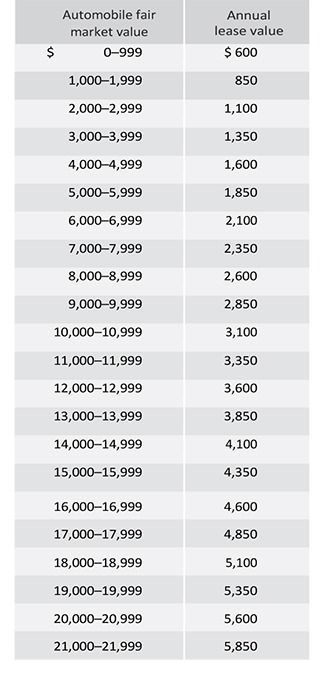
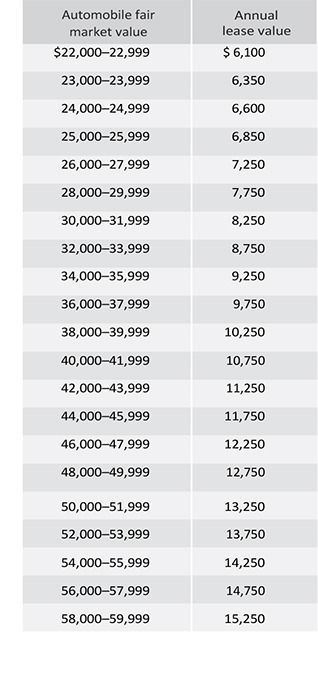
For vehicles having a fair market value in excess of $59,999, the annual lease value is equal to: (.25 x automobile fair market value) + $500.
At Rose Financial Solutions, we deliver tax solutions that are proactive, manage risk, maintain compliance, and minimize tax expense. Our team is comprised of experienced certified public accountants and tax professionals who stay up-to-date on current and future tax regulations and tax strategies at the federal, state, and local levels. Contact us for more information on how we can configure a cost-effective tax solution based on your current financial position as well as your future financial plans.
Visit Us On:





